The liver, a vital organ situated in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen, plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health.
It performs over 500 essential functions, including detoxification, metabolism of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates, bile production for digestion, and storage of vitamins and minerals. However, when an excessive amount of fat accumulates within its cells, the liver’s efficiency can be severely compromised. According to Dr. Nguyen Anh Tuan, Head of the Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery at Central Military Hospital 108, the liver is officially considered “fatty” when fat constitutes more than 5–10% of its total weight.
This accumulation is not merely an aesthetic concern; it makes the liver more vulnerable to various forms of damage. Prolonged fat buildup can lead to inflammation, a state where the liver becomes irritated and swollen. If left unchecked, this inflammation can progress to fibrosis, the thickening and scarring of liver tissue, which eventually can lead to more severe conditions like cirrhosis, and in dire cases, even liver failure.
The rising prevalence of fatty liver disease, particularly Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), is a significant public health concern globally, often linked to modern lifestyles characterized by poor diet and lack of physical activity. Dr. Tuan strongly emphasizes that while medical intervention may be necessary in advanced stages, “dietary and lifestyle changes can significantly improve the condition.” This highlights the profound impact of daily choices on liver health.
Fortunately, integrating specific natural foods into one’s diet can actively support liver recovery and help combat fat accumulation. This article will explore six expert-recommended foods that are known for their beneficial properties in supporting liver health and aiding in the fight against fatty liver disease, detailing their mechanisms of action and how they can be incorporated into your daily meals.
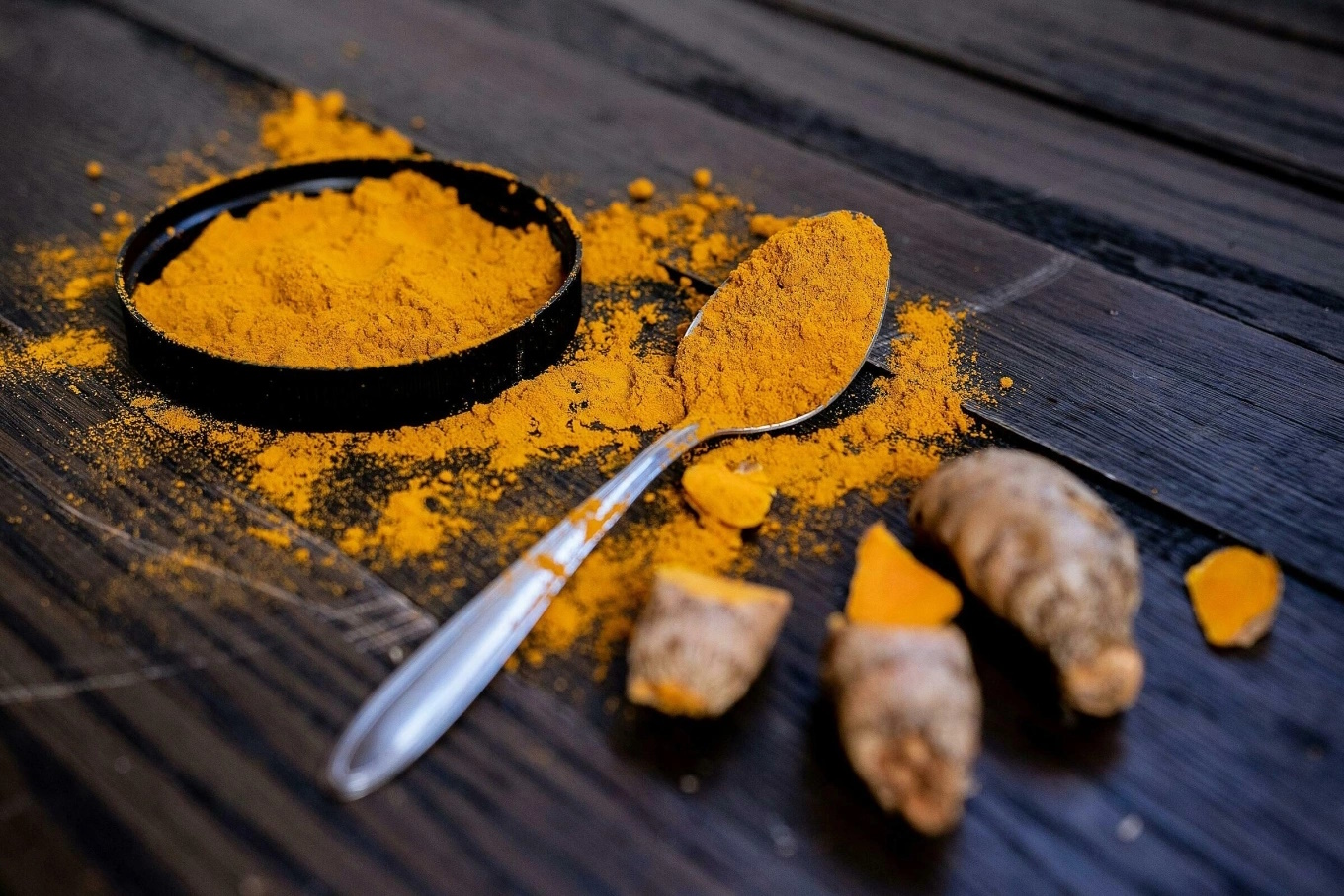
1. Turmeric: The Metabolic Booster
Turmeric, a vibrant golden spice, is celebrated for its potent anti-inflammatory and metabolic properties that can aid liver health.
Enhancing Fat Metabolism in the Liver
Turmeric, a golden-yellow spice widely used in Asian cuisine and traditional medicine, is highly regarded for its profound benefits for liver health. Its primary active compound, curcumin, is a powerful antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent. In the context of fatty liver disease, turmeric plays a crucial role by actively helping to prevent fat buildup in the liver. It achieves this by significantly boosting fat metabolism. This means that turmeric helps the liver process fats more efficiently, breaking them down and utilizing them for energy rather than storing them within its cells.
By enhancing the liver’s metabolic pathways, curcumin can effectively reduce the accumulated fat content within the liver. This action is vital because the core problem in fatty liver disease is the excessive storage of triglycerides in liver cells. Studies suggest that curcumin can influence various genes and proteins involved in lipid metabolism, promoting the oxidation of fatty acids and inhibiting lipogenesis (the formation of new fats).
Regular incorporation of turmeric into your diet, whether through cooking or as a supplement, can provide a natural and effective way to support your liver’s ability to process fats, thereby mitigating the progression of fatty liver disease and promoting a healthier hepatic environment.
2. Lime: The Detoxification Ally
Limes are packed with vital nutrients that specifically support the liver’s detoxification processes and reduce inflammation.
Boosting Glutathione and Reducing Inflammation
Limes are not just a flavorful addition to drinks and dishes; they are powerhouse fruits, exceptionally rich in Vitamin C. This essential vitamin acts as a powerful natural antioxidant. In the context of liver health, Vitamin C plays a critical role by stimulating the liver’s production of glutathione. Glutathione is often referred to as the body’s “master antioxidant” and is a key compound for detoxification.
It helps the liver neutralize harmful toxins and eliminate them from the body, thereby reducing the burden on the liver. A healthy supply of glutathione is crucial for the liver’s ability to effectively cleanse the bloodstream and prevent cellular damage.
Beyond Vitamin C, limes also contain other beneficial compounds, notably naringenin. Research has indicated that naringenin possesses properties that can reduce liver inflammation specifically linked to fatty liver disease. Inflammation is a significant concern in fatty liver, as it can lead to further damage and scarring (fibrosis). By helping to quell this inflammation, naringenin contributes to protecting liver cells and preventing the progression of the disease. Incorporating limes into your daily diet—perhaps by adding a squeeze to water, tea, or salads—provides a refreshing way to support your liver’s natural detoxification capabilities and combat inflammation.
3. Apple Cider Vinegar: The Weight Management Aid
Apple cider vinegar is a popular natural remedy, often lauded for its ability to aid in weight loss, a key factor in managing fatty liver.
Supporting Weight Loss and Fat Reduction
Apple cider vinegar (ACV) has garnered significant attention in the natural health community and is widely regarded as a natural remedy for fatty liver disease. While the direct mechanisms on the liver are still being researched, its primary benefit in this context is its potential to aid in weight loss. Excess body weight, particularly obesity, is a leading risk factor for fatty liver disease, especially non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Therefore, any intervention that promotes healthy weight management can indirectly but significantly improve liver health.
ACV is believed to support weight loss through several mechanisms. It may help increase satiety, making you feel fuller for longer after meals, thereby reducing overall caloric intake. It can also help regulate blood sugar levels after meals, preventing sharp spikes and crashes that often lead to increased cravings and fat storage. By fostering a healthier metabolic environment and assisting with appetite control, ACV can contribute to a gradual and sustainable reduction in body fat.
This in turn helps to reduce fat storage specifically in the liver. While ACV should not be seen as a standalone cure, its incorporation into a balanced diet and healthy lifestyle can be a supportive measure in managing and improving fatty liver condition. It’s often consumed diluted in water before meals.
4. Green Tea: The Antioxidant Powerhouse
Green tea is renowned for its high antioxidant content, which directly benefits fat burning and reduces the risk of fatty liver disease.
Combating Fat and Preventing NAFLD
Green tea is a highly celebrated beverage globally, cherished for its rich concentration of antioxidants and essential nutrients. Among its most potent compounds are catechins, particularly epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), which are powerful polyphenols responsible for many of green tea’s health benefits. In the context of liver health and fat metabolism, green tea actively supports fat burning.
EGCG is known to enhance thermogenesis (the body’s production of heat), which increases energy expenditure and promotes the oxidation of fats for fuel. This means that green tea can help your body utilize stored fat more efficiently, reducing overall fat accumulation.
Furthermore, regular consumption of green tea has been shown to be particularly beneficial in reducing the risk of fatty liver disease, especially non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). NAFLD is often associated with metabolic syndrome, insulin resistance, and obesity. The antioxidants in green tea help combat oxidative stress in the liver, which is a key factor in the progression of fatty liver disease to more severe conditions like inflammation and fibrosis.
By promoting healthy fat metabolism, improving insulin sensitivity, and providing robust antioxidant protection, green tea acts as a powerful preventative and supportive agent for liver health. Incorporating a few cups of unsweetened green tea into your daily routine can be a simple yet effective dietary strategy for liver protection.
5. Dandelion: The Traditional Liver Tonic
Dandelion, traditionally used in herbal medicine, offers properties that support fat breakdown and activate liver function.
Activating Liver Function and Fat Breakdown
Dandelion is much more than just a garden weed; it is a plant with a long history of traditional use in herbal medicine, particularly as a “liver tonic.” Its roots and leaves are rich in various bioactive compounds, including bitter principles, flavonoids, and triterpenes, which contribute to its therapeutic effects.
For individuals struggling with fatty liver disease, dandelion is believed to be particularly beneficial as it supports fat breakdown within the liver. It aids in stimulating bile production and flow, which is essential for the digestion and absorption of fats. Improved bile flow can help in the emulsification of fats, making them easier for the body to process and eliminating them more efficiently.
Moreover, dandelion is thought to help activate liver function more broadly. It may assist in cleansing the liver by promoting the elimination of toxins and metabolic waste products. This “activation” can improve the overall efficiency of liver cells in performing their many metabolic roles.
It is considered particularly effective for individuals with NAFLD related to obesity, as it can support the body’s natural processes for managing fat and promoting liver health. Incorporating dandelion into your diet might involve consuming dandelion tea, using its leaves in salads, or taking it in supplement form, under guidance. Its traditional use points to its potential as a natural aid in promoting a healthier, more functional liver.
6. Papaya: The Healing Fruit
Papaya, including its seeds, is believed to possess compounds that aid in repairing liver damage and reducing fat in the liver.
Repairing Liver Damage and Burning Liver Fat
Papaya, a tropical fruit known for its vibrant color and sweet flavor, is increasingly recognized for its potential benefits in healing liver damage. Both the fruit itself and its less commonly consumed seeds are believed to contain powerful enzymes and compounds that contribute to liver recovery.
Papain and chymopapain, enzymes found abundantly in papaya, are known for their digestive and anti-inflammatory properties. These enzymes may help in breaking down proteins and promoting a healthier digestive environment, which can indirectly reduce the burden on the liver.
More directly, papaya is thought to aid in healing liver damage, including fibrosis. Fibrosis is a serious concern in fatty liver disease, representing the scarring of liver tissue that can impair its function. While research is ongoing, some traditional and preliminary studies suggest that compounds in papaya may help mitigate this scarring process.
Furthermore, the fruit is believed to contribute to burning fat in the liver. This effect could be attributed to its overall high antioxidant content, which helps combat oxidative stress, and its ability to support metabolic processes that reduce fat accumulation. As such, papaya is considered beneficial for managing fatty liver disease, offering a natural dietary approach to support hepatic health and potentially reverse some of the damage caused by fat buildup. Enjoying fresh papaya regularly or even incorporating small amounts of its seeds (often ground) into your diet can be a flavorful way to contribute to your liver’s well-being.
Expert Recommendations: Lifestyle for Liver Health
Beyond specific foods, overall dietary and lifestyle adjustments are crucial for managing fatty liver disease effectively.
Weight Management and Fat Intake Control
Dr. Nguyen Anh Tuan provides crucial overarching advice for patients dealing with fatty liver disease, emphasizing that dietary changes extend beyond just incorporating specific beneficial foods. His core recommendations revolve around two fundamental pillars: monitoring and managing body weight and limiting overall fat intake.
For individuals who are overweight or obese, which are primary risk factors for NAFLD, Dr. Tuan stresses that gradual weight loss is key to improving liver function and overall health. Rapid weight loss, conversely, can sometimes paradoxically worsen liver fat in the short term, so a slow, steady approach is generally recommended.
Monitoring weight involves consistent tracking to ensure progress towards a healthier body mass index (BMI). Limiting fat intake means choosing leaner protein sources, opting for healthy unsaturated fats in moderation, and significantly reducing consumption of saturated and trans fats, which are prevalent in processed foods, fried items, and certain animal products.
These dietary adjustments reduce the amount of fat the liver has to process and store, alleviating its burden. The focus should be on a balanced diet rich in whole foods, lean proteins, fruits, vegetables, and complex carbohydrates.
Broader Lifestyle Changes for Recovery
While specific foods and weight management are critical, Dr. Tuan’s broader emphasis on “dietary and lifestyle changes” underscores a holistic approach to liver recovery. Beyond just what you eat, lifestyle adjustments play an equally vital role:
- Regular Physical Activity: Engaging in consistent exercise, even moderate activities like brisk walking, can significantly help in burning calories, reducing body fat (including liver fat), improving insulin sensitivity, and enhancing overall metabolic health. Exercise helps utilize glucose and fatty acids more efficiently, preventing them from being stored as fat in the liver.
- Avoiding Alcohol: For alcoholic fatty liver disease, complete abstinence from alcohol is mandatory. Even for NAFLD, reducing or eliminating alcohol intake is highly recommended, as alcohol can exacerbate liver damage and inflammation.
- Hydration: Drinking sufficient water helps the body’s natural detoxification processes and supports overall cellular function, including liver cells.
- Balanced Diet: A general shift towards a Mediterranean-style diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats (like olive oil), while low in refined sugars, processed foods, and unhealthy fats, is often recommended. Avoiding sugary drinks and foods high in fructose is particularly important, as fructose metabolism primarily occurs in the liver and can contribute to fat accumulation.
- Consulting Healthcare Professionals: It is essential for patients with fatty liver disease to work closely with their doctors or a registered dietitian. They can provide personalized dietary plans, monitor progress, and adjust strategies as needed. This professional guidance ensures that interventions are safe, effective, and tailored to individual health conditions.
By combining the strategic inclusion of liver-friendly foods with comprehensive dietary and lifestyle modifications, individuals can significantly improve their fatty liver condition, protect their liver from further damage, and enhance their overall well-being.
Holistic Approach to Liver Health
Fatty liver disease, a growing health concern, highlights the critical importance of diet and lifestyle in maintaining hepatic well-being. As emphasized by Dr. Nguyen Anh Tuan, when fat accounts for more than 5-10% of the liver’s weight, it becomes susceptible to inflammation, fibrosis, and severe damage. Fortunately, incorporating specific foods and adopting holistic lifestyle changes can profoundly aid in recovery.
The six power foods – turmeric, lime, apple cider vinegar, green tea, dandelion, and papaya – each offer unique benefits. Turmeric boosts fat metabolism, while lime enhances detoxification through glutathione. Apple cider vinegar assists in weight loss and reduces liver fat, and green tea’s antioxidants combat fat accumulation and prevent NAFLD. Dandelion supports fat breakdown and liver function, and papaya aids in healing liver damage and burning liver fat.
These natural ingredients, when integrated into a balanced diet, serve as powerful allies. Combined with crucial advice on weight management, limiting fat intake, regular exercise, and professional guidance, these dietary and lifestyle adjustments offer a comprehensive and effective strategy for combating fatty liver disease, promoting liver recovery, and fostering long-term health.