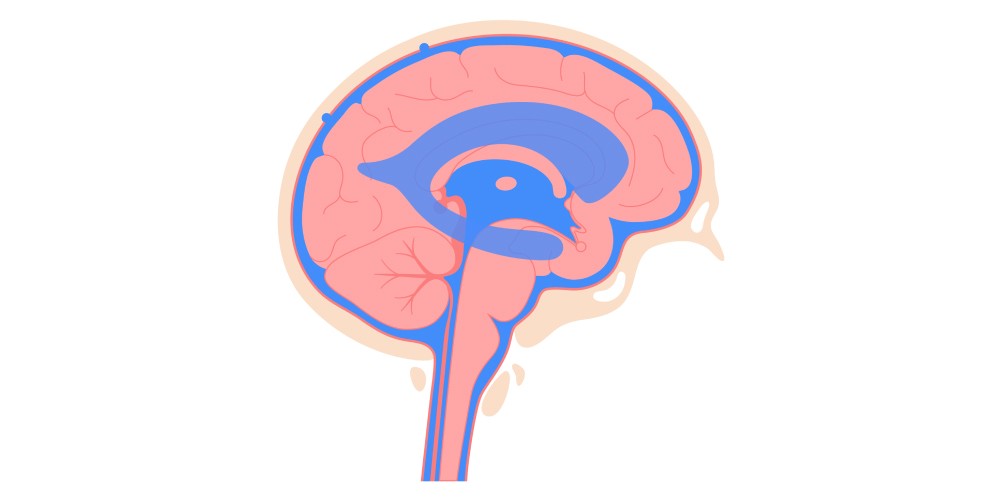
Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus Disease is a unique brain issue. It impacts many older individuals. Fluid accumulates in the brain. This fluid is cerebrospinal fluid, or CSF. CSF normally flows through the brain. It also surrounds the spinal cord. In NPH, this flow is disturbed. This causes ventricles to grow larger. Ventricles are fluid-filled spaces.
Despite this growth, pressure remains normal. This gives it the “normal pressure” name. Understanding Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus Disease is vital. Prompt diagnosis greatly aids patients. Helpful treatments are available. These treatments can enhance life quality. So, recognizing symptoms is key.
What Defines Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus Disease?
Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus Disease is a brain disorder. It involves too much CSF. CSF typically guards the brain. It clears waste products. It also cushions the brain. In NPH, excess CSF builds up. This expands the brain’s ventricles. Brain tissue becomes squeezed. This compression causes symptoms to appear.
Still, CSF pressure in the brain often stays normal. This makes NPH challenging to grasp. It complicates its diagnosis. It also sets NPH apart from other hydrocephalus forms. Other forms involve high pressure. NPH is often wrongly identified. It can be mistaken for Alzheimer’s. It can also be confused with Parkinson’s. Thus, precise diagnosis is essential. Many individuals live with NPH undiagnosed.
Primary Indicators of Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus Disease
Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus Disease shows a classic set of three signs. These three indicators frequently occur together. Spotting them is crucial for identification.
Walking Challenges
Trouble with walking is very prevalent. This is a main indicator. Patients might drag their feet. They may walk with a wide stance. They can seem unstable. Balance problems are common. They might fall often. This indicator typically appears first. It can worsen over time. It affects daily activities. Walking can become very slow. It can also be very difficult. This walking style often resembles Parkinson’s. Yet, it responds differently to treatment. Mobility is significantly reduced. This impacts self-reliance. Hence, careful assessment is necessary.
Bladder Control Issues
Loss of bladder control is another frequent sign. Patients may urinate often. They might feel a strong urge to go. This can lead to accidents. They might not reach the toilet in time. This indicator can be embarrassing. It affects social interactions. It can also impact personal cleanliness. This can lead to feeling isolated. It often shows up after walking problems. Still, it is a significant indicator. It suggests NPH.
Thinking Decline or Cognitive Shifts
Cognitive issues also arise. Memory problems are common. Patients might forget recent events. They can struggle with new facts. Thought processes may slow down. They might have trouble concentrating. Problem-solving abilities can lessen. They might also lose interest in hobbies. Executive functions are often impaired.
This impacts planning daily tasks. It can also affect making choices. These cognitive changes mirror other forms of dementia. Alzheimer’s disease is a frequent misdiagnosis. However, NPH-related cognitive decline can be reversible. This potential for reversal makes prompt identification vital.
Origins and Susceptibility Factors of Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus Disease
The exact reason for Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus Disease is often unknown. This is termed idiopathic NPH. It is the most frequent type. Sometimes, NPH can stem from other health issues.
Potential Underlying Origins
Brain injury can cause NPH. Head trauma is an instance. Brain bleeding can also lead to NPH. Hemorrhage in the brain is very harmful. Infections are another reason. Meningitis can inflame brain coverings. This affects CSF circulation. Brain tumors can obstruct CSF pathways. Surgery can also sometimes result in NPH. This includes operations on the brain. Inflammation can also play a part. So, a thorough health history is important.
Susceptibility Factors
Age is a key susceptibility factor. NPH mainly affects older individuals. It is more common in those over sixty. Certain health conditions heighten risk. High blood pressure can contribute. Diabetes might also have a role. Heart disease could be a factor. A family background of NPH is not common. However, some genetic tendencies may exist. More studies are still required. Overall, understanding susceptibility factors raises awareness. This aids in early detection.
Identifying Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus Disease
Identifying Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus Disease is intricate. It demands multiple tests. A comprehensive evaluation is essential. This prevents misdiagnosis.
Clinical Examination
A doctor will perform a physical check. They will also gather a detailed health history. They will ask about indicators. They will inquire about their beginning. They will also ask about indicator progression. A neurological check is critical. It assesses walking. It verifies balance. It gauges cognitive ability. It also tests reflexes. This initial review guides subsequent actions.
Imaging Scans
Brain imaging is crucial. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is preferred. MRI reveals expanded ventricles. It can also exclude other ailments. These include growths or strokes. Computed Tomography (CT) scans can also be used. They show similar findings. Yet, MRI offers more details. It provides a clearer view of brain structures. These images confirm ventricle growth. But, they do not confirm normal pressure.
Lumbar Puncture (Spinal Tap Procedure)
A lumbar puncture is a vital identification test. CSF is withdrawn from the spinal column. This measures pressure. Fluid is also collected for analysis. Sometimes, a large amount of CSF is removed. This is called a high-volume tap. Doctors then observe indicator changes. If indicators improve, NPH is more probable. This improvement is often brief. It confirms potential shunt surgery benefits. A positive tap predicts good surgical results.
CSF Infusion Assessment
This assessment is more specialized. It gauges how CSF is absorbed. Saline is infused into the spinal canal. Pressure alterations are watched. This helps evaluate CSF dynamics. It helps spot absorption issues. This assessment is highly predictive. It shows shunt responsiveness.
External Lumbar Drainage (ELD)
In some instances, an ELD is used. A small tube drains CSF for several days. This happens in a hospital. Indicators are monitored daily. Significant improvement suggests NPH. It also strongly indicates shunt benefit. This is a very reliable assessment. It can confirm the identification. It guides treatment choices.
Management Approaches for Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus Disease
Managing Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus Disease often involves an operation. Shunt placement is the primary method. It aims to lessen CSF build-up.
Shunt Placement
A shunt is a medical device. It is a slender, flexible tube. It is surgically placed in the brain. One end enters a ventricle. The other end drains CSF. It can drain to the abdomen. It can also drain to the heart. A valve regulates CSF flow. This valve stops too much or too little drainage. Shunt placement can markedly improve indicators.
Walking problems often improve first. Bladder control also gets better. Cognitive function can also show progress. This is a key advantage of identification. It provides hope for recovery.
Shunt Variations
Several types of shunts exist. Ventriculoperitoneal (VP) shunts are common. They drain CSF to the abdomen. Ventriculoatrial (VA) shunts drain to the heart. Programmable valves are frequently used. These valves allow external flow adjustments. This avoids extra operations. It permits doctors to fine-tune drainage. This optimizes indicator relief.
Risks of Shunt Operations
Like all operations, shunts carry risks. Infection is a concern. Shunt dysfunction can occur. This includes blockages or breaks. Too much or too little drainage can happen. Too much drainage can cause headaches. It can also lead to other problems. Too little drainage means indicators continue. Revisions might be necessary. However, benefits often outweigh risks.
Non-Surgical Strategies
Non-surgical methods are not primary. They do not fix the root problem. Diuretics might be used sometimes. These medicines lessen fluid. However, they are generally ineffective for NPH. Physical therapy is often advised. It helps manage walking difficulties. Occupational therapy assists with daily tasks. Cognitive therapy can support memory. These therapies enhance life quality. They complement surgical management. They do not replace it.
Thriving with Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus Disease
Thriving with Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus Disease can be tough. But, with proper management, life improves. Ongoing oversight is important.
Post-Operation Care
After shunt placement, regular follow-up is necessary. Doctors monitor shunt operation. They check for indicator changes. Adjustments to the shunt valve may be needed. This fine-tunes CSF drainage. Rehabilitation is also crucial. Physical therapy helps restore movement. Occupational therapy aids daily living skills. Speech therapy can assist if required. Support groups offer emotional aid. They link patients with similar experiences.
Long-Term View
The long-term view for NPH varies. It depends on several aspects. Early identification improves results. Prompt management is also key. Some patients experience significant healing. They regain much ability. Others see partial progress. Indicators might stabilize. NPH is usually not progressive after shunt. However, some cognitive decline may persist.
Continuous medical attention is crucial. It ensures the best possible life quality. Regular checking helps prevent complications. It optimizes long-term health.
Optimism for Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus Disease
Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus Disease is a serious condition. It affects many older individuals. It causes a distinct set of indicators. These include walking issues, bladder problems, and thinking decline. Accurate and early identification is vital. It often requires specific assessments.
The most effective management is shunt placement. This operation can markedly improve indicators. It provides hope for many patients. Understanding NPH is essential. It allows for timely action. This leads to superior patient outcomes. Always consult a medical expert for identification. They can offer suitable care.